Introduction
![]()
Bird eggs are remarkable reproductive structures produced by various species of birds. These oval-shaped wonders vary in size, color, and texture, reflecting the diversity of bird species around the world. Serving as protective enclosures for developing embryos, bird eggs play a vital role in the continuation of avian life.
The predation of bird eggs is not only a fundamental aspect of the natural food web but also provides valuable insights into the delicate balance of nature. By studying the predators that consume bird eggs, we can gain a deeper understanding of avian ecology, behavior, and the challenges faced by birds during the nesting season.
The Importance of Predation

Predators that feed on bird eggs play a crucial role in controlling bird populations and preventing overpopulation, contributing to the overall health and stability of ecosystems. Moreover, the predation of bird eggs can have significant implications for specific bird species, especially those that are endangered or vulnerable. Identifying the predators that target bird eggs allows us to develop targeted conservation strategies to protect these at-risk species and preserve their ecosystems.
Insights into Avian Biology

Studying what eats bird eggs contributes to our broader knowledge of avian biology. Research on the various predators of bird eggs provides insights into predator-prey dynamics, nesting behaviors, and the strategies birds employ to defend their eggs. These findings deepen our understanding of the complex interactions within ecosystems and shed light on the remarkable adaptations and survival strategies of birds.
Exploring the World of Bird Eggs
![]()
In this blog post, we will embark on a fascinating journey into the world of bird eggs and the predators that prey upon them. We will explore the different types of animals that consume bird eggs, including mammals, reptiles, other birds, and even insects. By delving into the diverse array of predators, we can gain a greater appreciation for the challenges faced by birds during nesting and the importance of safeguarding their fragile offspring.
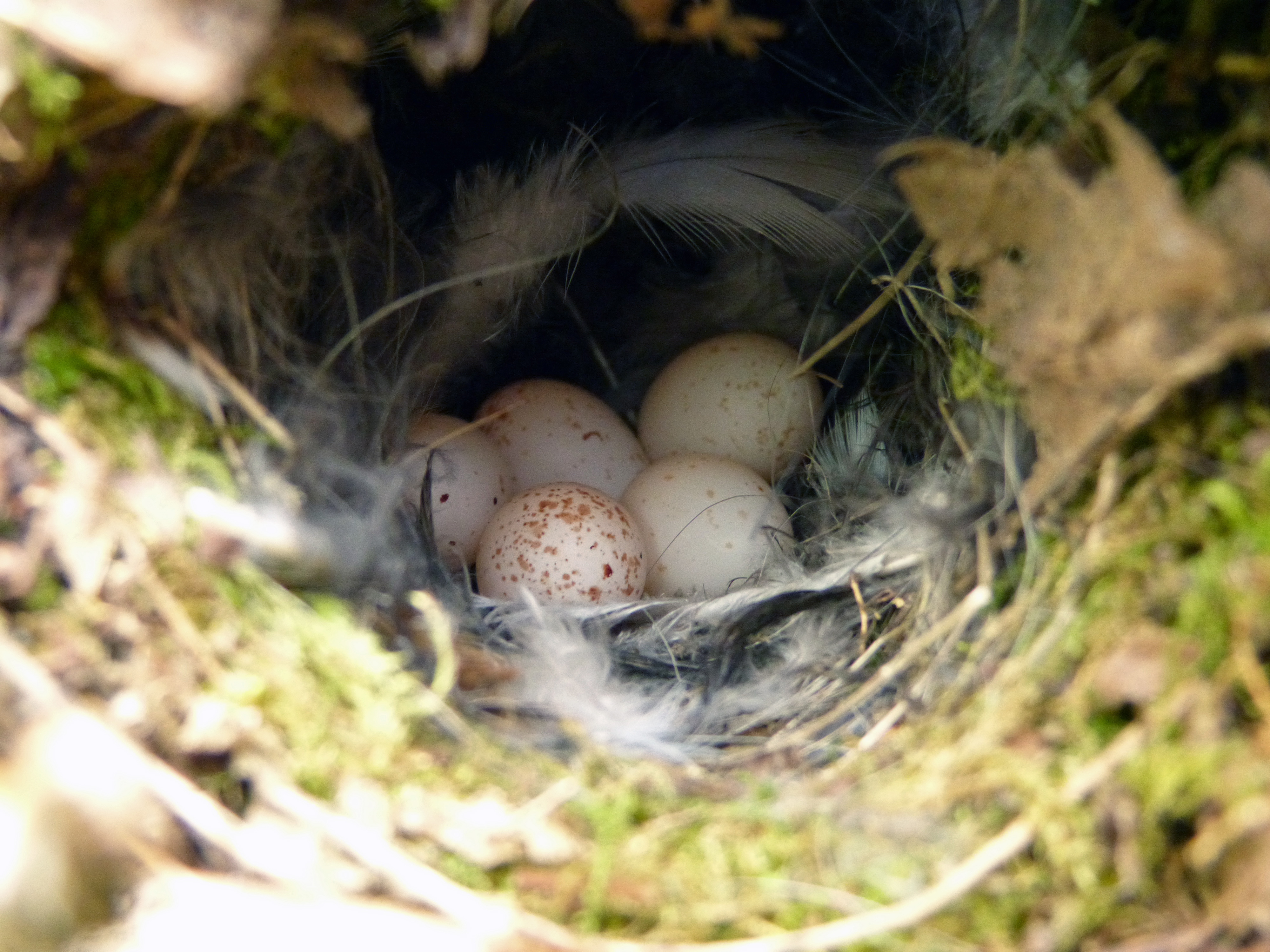
Types of Bird Eggs

Bird eggs exhibit an incredible diversity in their appearance, reflecting the wide range of bird species that lay them. By identifying common bird eggs, describing their physical characteristics, and exploring their variety, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of avian reproduction.
Identifying Common Bird Eggs
To begin, let’s delve into the most common bird species that lay eggs. Among the well-known examples are robins, sparrows, pigeons, ducks, and chickens. These species represent a fraction of the avian diversity, but they provide a starting point for understanding bird eggs.
When identifying bird eggs, it’s helpful to consult field guides, ornithology resources, and reputable websites. These sources offer accurate information about bird species and their eggs, helping us recognize the unique characteristics of each species’ eggs.
Describing the Physical Characteristics of Bird Eggs
Bird eggs exhibit a remarkable range of physical characteristics. They come in various sizes, shapes, colors, and surface textures.
-
Size: Bird eggs span a vast size range, from the diminutive eggs of hummingbirds to the substantial eggs of ostriches. This diversity in size is a reflection of the different breeding strategies and body sizes of bird species.
-
Shape: The shape of bird eggs can vary significantly. While many eggs are oval or elongated, others may be spherical or conical. These distinctive shapes are adaptations that help the eggs fit snugly in the nest and prevent rolling.
-
Color: The coloration of bird eggs is equally diverse. Eggs can be plain white or beige, but they also come in an array of patterns, markings, and hues. Some eggs are speckled or mottled, while others display vibrant colors. These color variations serve multiple purposes, including camouflage, thermoregulation, and signaling.
-
Surface Texture: The surface texture of bird eggs can be smooth, textured, or have a matte or glossy appearance. The texture plays a role in facilitating gas exchange and maintaining the integrity of the eggshell.
-
Shell Thickness: Bird eggshells can vary in thickness depending on the species. Some eggs have relatively thin shells, while others possess thicker and more robust shells. Shell thickness is influenced by factors such as predation pressure and the need for protection during incubation.
Exploring the Variety of Different Bird Eggs

Bird eggs exhibit an assortment of unique patterns and markings, helping birds camouflage their eggs and make them less conspicuous to potential predators. Some species lay eggs that mimic the surrounding environment, blending seamlessly with their nest or habitat. Others incorporate patterns and markings that resemble foliage or provide disruptive coloration, making it harder for predators to spot the eggs.
By exploring the diversity of bird eggs, we gain a deeper understanding of the remarkable adaptations and strategies that birds have developed over millions of years. Each egg represents a delicate and vital step in the continuation of avian life.
In the next section, we will shift our focus to the predators that pose a threat to bird eggs and examine their behaviors and impact.
Predators of Bird Eggs

Bird eggs are a valuable food source for various predators, and understanding their behaviors is crucial for comprehending their impact on bird populations.
Common Predators
Several animals are known for preying on bird eggs:
-
Snakes: Rat snakes and racers are skilled climbers, enabling them to raid bird nests and consume eggs effectively.
-
Mammals: Rats, squirrels, raccoons, opossums, skunks, foxes, and weasels are among the mammals that pose a threat to bird eggs. They can locate and raid nests, causing significant damage.
-
Reptiles: Opportunistic predators like lizards and turtles may consume bird eggs when given the chance, endangering their survival.
-
Amphibians: Frogs and toads, especially in wetland habitats, are known to consume bird eggs laid in shallow water.
-
Invertebrates: Ants and beetles, although individually small, can exploit bird nests and consume eggs, leading to a cumulative impact.
Predator Behaviors
Predators employ various strategies to access bird eggs while minimizing the risk of detection:
-
Nest Raiding: Predators actively target bird nests by climbing trees, entering cavities, or digging into ground nests.
-
Stealth and Camouflage: Many predators possess adaptations that allow them to approach nests undetected, reducing the chance of being spotted by parent birds.
-
Timing: Predators often time their attacks when parent birds are away from the nest, increasing their chances of successfully obtaining eggs.
Impact on Bird Eggs
Predators play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling prey populations. However, their presence can have negative implications:
-
Ecological Balance: Predators prevent overpopulation of prey species, thus maintaining ecosystem balance.
-
Population Dynamics: High predation rates can lead to reduced reproductive success and population declines among bird species.
-
Conservation Concerns: Understanding the impact of predators on bird eggs is vital for conservation efforts. Implementing strategies to mitigate predation can help protect vulnerable bird populations.
By recognizing common predators, understanding their behaviors, and assessing their impact, researchers, conservationists, and bird enthusiasts can develop effective strategies to safeguard bird eggs and promote healthy avian populations.
Human Impact on Bird Eggs

Human activities have significantly threatened the survival of many bird species through habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution.
Habitat Destruction
Deforestation and urbanization have dire consequences for bird eggs. Loss of nesting sites decreases egg survival rates and disrupts breeding patterns. Crucial habitats like wetlands, forests, and grasslands are destroyed, leaving birds more vulnerable to predation and exposure. Fragmentation of habitats exacerbates the problem, leading to increased competition among bird species and higher risks of egg predation.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to bird eggs. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns disrupt breeding seasons and food availability for birds. Extreme weather events directly impact bird nests, causing damage or destruction of eggs. Moreover, shifts in temperature and weather patterns affect the timing of peak food availability, resulting in reduced egg production and lower survival rates.
Pollution
Pollution in various forms adversely affects bird eggs. Pesticides and herbicides contaminate food sources and nesting environments, reducing egg viability and increasing embryo mortality. Air pollution accumulates in bird habitats, contaminating eggs and interfering with their development and hatching success. Chemical pollutants like heavy metals and PCBs accumulate in bird tissues, including eggs, causing reproductive failures and reduced hatching success.
These human-induced impacts on bird eggs necessitate urgent conservation efforts to mitigate the damage and preserve avian populations.
Conservation Efforts for Bird Eggs
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting bird eggs and their nesting sites have gained significant momentum in recent years. Various organizations and initiatives have emerged, dedicated to safeguarding these fragile treasures of nature. These efforts focus on preserving habitats that are crucial for bird nesting and egg-laying, such as forests, wetlands, and grasslands.
Exploring Existing Conservation Efforts
One key aspect of bird egg conservation is the implementation of laws and regulations that prevent the destruction or disturbance of bird nests and eggs. These legal measures serve to deter activities that could harm nesting sites and disrupt the delicate balance of bird populations. Additionally, monitoring and research programs have been established to study bird populations, nesting behaviors, and the threats faced by eggs. By understanding the challenges that bird eggs encounter, conservationists can develop effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
Collaboration is another vital component of conservation efforts. Organizations work closely with landowners, government agencies, and local communities to create protected areas and promote responsible land management practices. By fostering partnerships, they can ensure the long-term preservation of habitats and the species that rely on them.
Discussing the Importance of Citizen Science

Citizen science plays a significant role in bird egg conservation by actively involving the public in data collection and monitoring. Birdwatchers, enthusiasts, and volunteers contribute to monitoring bird nests, recording breeding activities, and reporting any disturbances or threats they observe. This valuable information helps researchers and conservationists gather crucial data on nesting success rates, species distribution, and population trends.
Through citizen science initiatives, individuals can make meaningful contributions to conservation efforts, even without formal scientific training. By engaging with the natural world and becoming advocates for birds and their eggs, citizens can play a vital role in protecting and preserving these delicate ecosystems.
Examining the Potential of Artificial Nests

Artificial nests, also known as nest boxes or birdhouses, offer an innovative solution to address the shortage of natural nesting sites. These man-made structures mimic natural nesting cavities that may be lacking in certain landscapes due to habitat loss or human activities. Artificial nests are particularly beneficial for cavity-nesting species such as woodpeckers, owls, and some songbirds.
Conservation organizations and individuals often install and maintain artificial nests in strategic locations to support bird populations. These structures provide safe and secure nesting opportunities, reducing competition for limited natural cavities. By providing alternative nesting sites, artificial nests help bolster breeding success and contribute to the overall conservation of bird eggs.
Conclusion

In this blog post, we have explored the fascinating world of bird eggs, their predators, human impact, and the importance of conservation efforts. Let’s recap the main findings and key points discussed throughout the article.
Summarizing the Information
We began by delving into what bird eggs are and why they capture people’s interest. Understanding the different types of bird eggs and their physical characteristics allowed us to appreciate the remarkable diversity present in avian reproduction.
Next, we examined the predators that pose a threat to bird eggs. By identifying common predators and discussing their behaviors, we gained insight into the challenges faced by nesting birds. The impact of predators on bird eggs highlighted the vulnerability of these delicate structures and their potential consequences for bird populations.
Moving on to human impact, we explored the effects of habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution on bird eggs. These factors pose significant threats to avian species, disrupting their breeding patterns and reducing their chances of successful reproduction. Recognizing these impacts is crucial for developing conservation strategies.
Exploring the Importance of Bird Eggs
Bird eggs play a vital role in avian reproduction and species survival. They serve as a crucial stage in the life cycle of birds, providing a protected environment for embryonic development. Bird eggs also contribute to maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance by sustaining bird populations and facilitating pollination and seed dispersal.
Providing Actionable Steps for Readers to Take
To protect bird eggs and contribute to their conservation, there are actionable steps that readers can take:
-
Create Safe Nesting Habitats: Provide suitable nesting sites in your backyard or local environment by installing birdhouses, nesting platforms, or natural nesting materials.
-
Install Predator Deterrents: Employ strategies such as predator guards, baffles, or netting to deter potential egg predators from accessing nests.
-
Support Conservation Organizations: Contribute to bird conservation efforts by supporting organizations focused on protecting bird habitats, conducting research, and implementing conservation initiatives.
-
Practice Responsible Bird-Watching and Photography: Minimize disturbance to nesting sites by maintaining a safe distance, using binoculars or telephoto lenses, and adhering to ethical guidelines for bird observation.
Concluding Thoughts

Raising awareness about the threats faced by bird eggs is crucial for their protection and the preservation of bird populations. By sharing the knowledge gained from this article with others, readers can play an active role in safeguarding these precious avian reproductive structures. Remember, it is our collective responsibility to protect bird eggs and ensure a sustainable future for our feathered friends.
Together, let’s celebrate the beauty and significance of bird eggs while taking meaningful action to safeguard their existence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common predators of bird eggs?
The most common predators of bird eggs include snakes, mammals such as rats and raccoons, reptiles like lizards and turtles, amphibians such as frogs and toads, and invertebrates like ants and beetles.
How do predators access bird nests and eggs?
Predators employ various strategies to access bird nests and eggs. They may climb trees, enter cavities, or dig into ground nests. Some predators possess adaptations that allow them to approach nests undetected, while others time their attacks when parent birds are away from the nest.
What is the impact of egg predation on bird populations?
Predation of bird eggs plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling prey populations. However, high predation rates can lead to reduced reproductive success and population declines among bird species, especially those that are endangered or vulnerable.
How can predators be deterred from accessing bird nests?

Predators can be deterred from accessing bird nests by employing strategies such as installing predator guards, baffles, or netting. Creating safe nesting habitats and providing alternative nesting sites like birdhouses can also help reduce predation risks.
What can be done to protect bird eggs from predators?
To protect bird eggs from predators, it is important to create safe nesting habitats, install predator deterrents, and support conservation organizations focused on bird conservation. Practicing responsible bird-watching and photography can also minimize disturbance to nesting sites and contribute to the protection of bird eggs.

Leave a Reply