Introduction
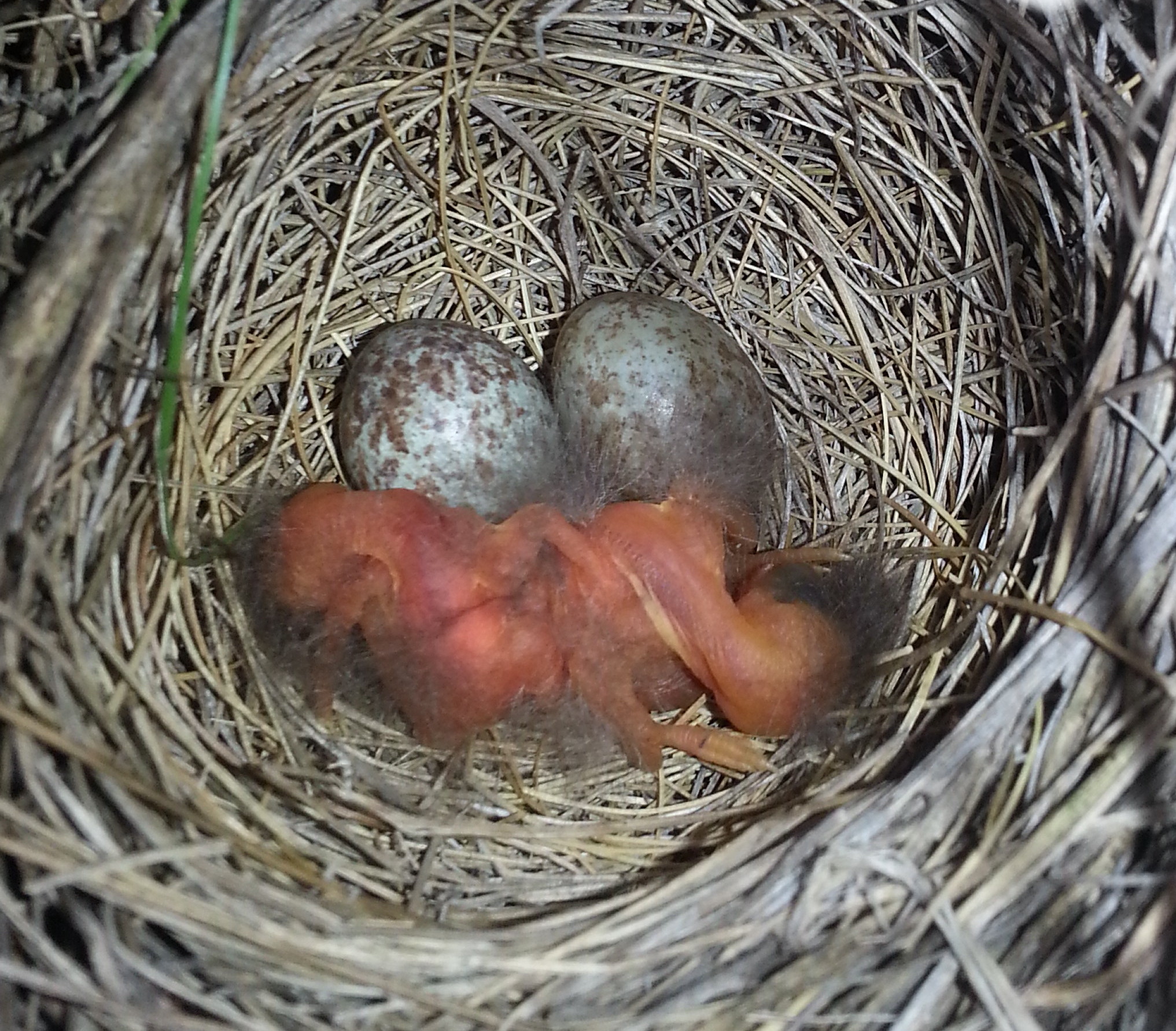

Birds construct remarkable nests as safe havens for laying eggs and nurturing their offspring. These nests exhibit incredible diversity in size, shape, and location, reflecting the unique adaptations and preferences of different bird species.
The hatching process of birds begins with incubation, a critical phase during which parent birds provide warmth and regulate the temperature to support the development of the embryos inside the eggs.
During incubation, parent birds take turns sitting on the eggs to maintain an optimal temperature range and protect them from extreme cold or heat. The duration of the incubation period varies significantly among bird species, influenced by factors such as egg size, metabolic rate, and environmental conditions.
When the embryos reach the final stages of development, a remarkable event called “pipping” occurs. Chicks inside the eggs start pecking at the shell using a specialized egg tooth or a small, hard protuberance on their beaks. Gradually, they break through the shell, demonstrating their resilience and determination.
Understanding the intricacies of bird nests and the hatching process provides a glimpse into the wonder of avian life. In the following sections, we will explore different types of bird nests, factors influencing hatching times, the average duration of hatching, and what to expect during this remarkable journey.
Types of Bird Nests
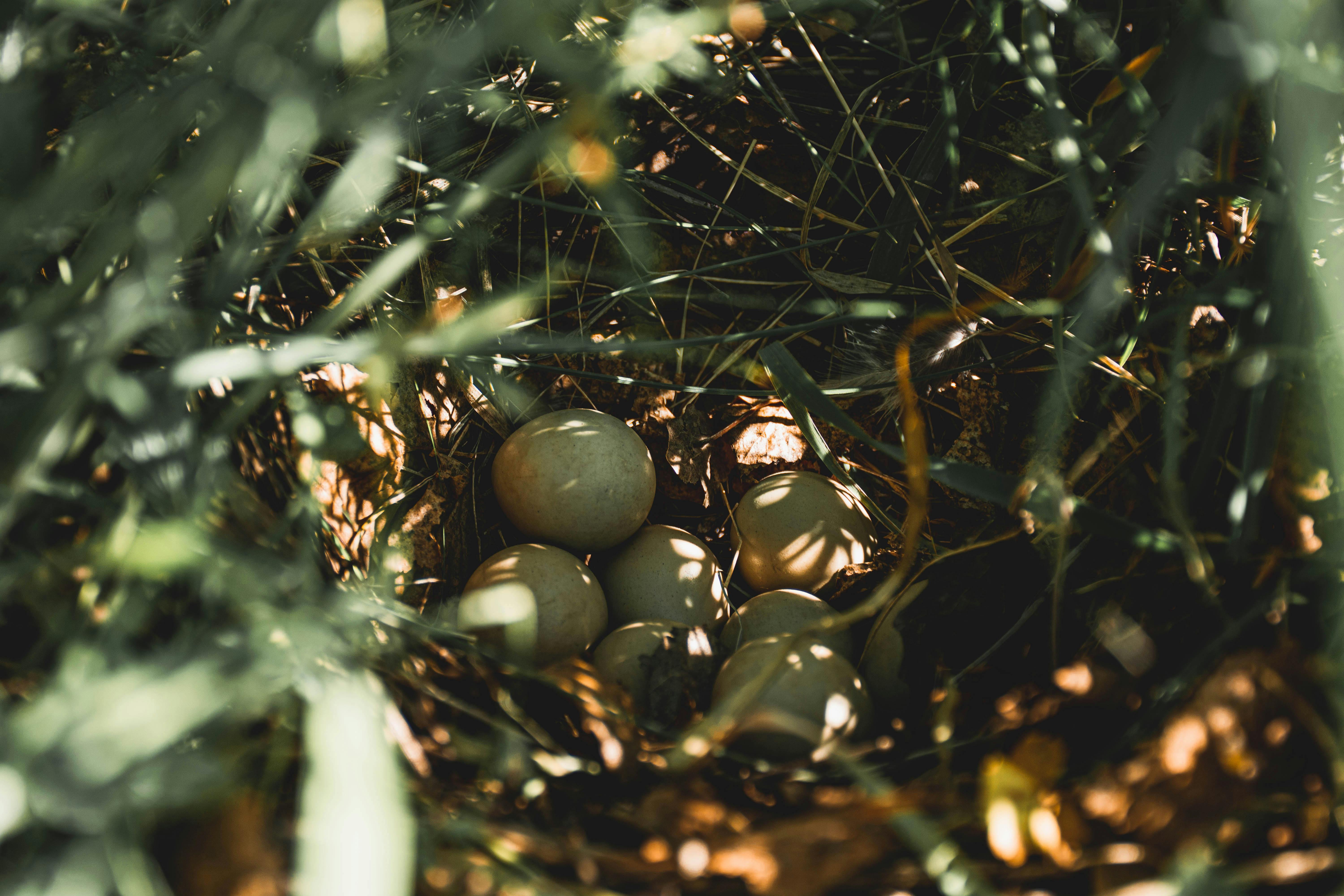

Birds exhibit remarkable diversity in nest-building behaviors, resulting in a wide array of nest types that influence the hatching process.
Open Cup Nests

The most common type of bird nest, open cup nests, are bowl-shaped structures built on tree branches or shrubs. Species like robins and sparrows construct these nests using materials such as grass, twigs, and leaves. Open cup nests offer protection and camouflage for the eggs.
Platform Nests
Platform nests have a flat structure and are often built on platforms made of sticks or twigs. They can be found in trees, cliffs, or man-made structures. Birds such as eagles and hawks construct platform nests, providing a sturdy foundation for their eggs.
Cavity Nests
Cavity nests are created within cavities, including tree hollows, crevices, or ground burrows. Woodpeckers, owls, and certain species of ducks demonstrate this nesting behavior. Cavity nests offer excellent protection against predators and harsh weather conditions.
Burrow Nests

Burrow nests are constructed in tunnels or burrows dug into the ground. Birds like kingfishers and certain species of penguins exhibit this nesting strategy, providing a secure and secluded environment for their eggs.
Hanging Nests
Hanging nests are suspended from tree branches and intricately woven using materials like grass, moss, and spider silk. Weaverbirds and oropendolas are well-known for their skill in creating hanging nests. These nests dangle from branches, offering protection against ground-dwelling predators.
The design and location of bird nests play a crucial role in the hatching process. Nests provide essential functions that can influence the duration of incubation and subsequent hatching of eggs.
-
Protection: Nests act as a protective barrier, shielding eggs from predators and environmental threats. The choice of nest type determines the level of protection provided.
-
Insulation: Nests help regulate the internal temperature and humidity surrounding the eggs. Different nest types exhibit varying insulating properties, affecting the rate of heat transfer.
Understanding the various types of bird nests and their impact on hatching times allows us to appreciate the remarkable adaptations that birds have developed to ensure successful reproduction. These nests contribute to the survival and propagation of avian species.
Factors That Influence Hatching Time
Hatching time in bird nests is determined by several key factors: temperature, humidity, number of eggs, and parental care. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in the successful development and hatching of bird eggs.
Temperature: A Delicate Balance

Temperature is critical for the hatching process. Different bird species have specific temperature requirements for optimal embryonic development. Maintaining the right temperature range is essential. Higher temperatures can speed up development, resulting in shorter incubation periods, while lower temperatures can delay hatching. Bird parents skillfully regulate the nest temperature by adjusting their incubation behavior to create the ideal conditions for embryonic growth.
Humidity: The Importance of Moisture

Humidity levels within the nest also impact hatching time. Adequate humidity is necessary to maintain the moisture content of the eggs during incubation. Deviations from optimal humidity levels can affect egg viability and hatching time. High humidity can prolong the incubation period, while low humidity can lead to premature hatching or egg desiccation. The parents actively manage the moisture within the nest environment to ensure the right humidity levels.
Number of Eggs: A Balancing Act

The number of eggs in a nest can influence hatching time. Generally, larger clutches have longer incubation periods compared to smaller clutches. With larger clutches, parent birds must distribute their attention and warmth among more eggs, slowing down the overall development process. Larger clutches may also experience increased competition for resources within the nest, potentially affecting hatching success. In contrast, smaller clutches allow for more focused parental care, creating optimal conditions for faster hatching.
Parental Care: Nurturing the Next Generation
The level of parental care significantly affects hatching time. Both male and female birds take turns incubating the eggs, ensuring consistent warmth and attention for proper development. Parental care involves regulating temperature and humidity, protecting the eggs from predators, maintaining the nest’s integrity, and providing food for the incubating partner. The quality and extent of parental care influence the overall health and viability of the eggs, thereby impacting hatching time.
Understanding these factors that influence hatching time is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of avian reproduction. By considering temperature, humidity, number of eggs, and parental care, we gain insight into the diverse strategies employed by bird species to ensure successful hatching. Next, let’s delve into the average hatching time of different bird species and explore the factors that can influence it.
Average Hatching Time

Birds display a remarkable range of incubation periods, influenced by various factors that shed light on their unique adaptations and ecological needs.
Variation Across Bird Species
Incubation periods differ significantly among bird species, spanning from as short as 10 to 12 days for small songbirds to as long as 80 days for certain albatross species.
-
Songbirds – Finches and sparrows have short incubation periods of 10 to 14 days due to their small eggs.
-
Waterfowl – Ducks and geese require around 25 to 35 days for their larger eggs to hatch.
-
Birds of prey – Eagles and hawks have an average incubation period of 35 to 45 days, attributed to their larger eggs and longer developmental periods.
-
Shorebirds – Sandpipers and plovers have relatively short incubation periods of 20 to 30 days, likely influenced by their small eggs and nesting habitats.
-
Albatrosses – These seabirds have the longest incubation periods, lasting 60 to 80 days, due to their large eggs and unique life history traits.
Factors Influencing Hatching Time
Several factors contribute to the variations in hatching time among bird species, providing insights into avian reproduction intricacies.
-
Bird species – Each species has evolved its own hatching time, reflecting genetic, physiological, and ecological factors crucial for successful reproduction.
-
Egg size – Larger eggs require more time to hatch due to increased nutrient content and the need for proper embryo development.
-
Environmental conditions – Nest temperature and humidity significantly impact incubation. Warmer temperatures accelerate development, while cooler temperatures prolong it. Adequate humidity maintains necessary moisture levels.
-
Nest predation – The risk of predation influences incubation behavior. Some species shorten the period to minimize vulnerability, while others extend it to increase chick survival outside the nest.
-
Parental care – The level of parental involvement affects hatching time. Species with attentive parents may have shorter incubation periods compared to those with less parental care.
Understanding average hatching time and its influencing factors provides a fascinating glimpse into avian reproduction strategies, deepening appreciation for birds’ efforts to ensure successful hatching and offspring survival.
What to Expect During the Hatching Process

During the hatching process, there are signs that indicate the imminent arrival of adorable little chicks. Understanding these signs can help you anticipate the exciting moment. Here are common signs of hatching:
-
Incubation period: The duration varies depending on the bird species, ranging from 10 to 50 days. Research the specific bird species for a more accurate estimate.
-
Vocalizations: As hatching nears, you may hear faint chirping or peeping sounds coming from the eggs. These sounds indicate that the chicks are becoming more active and ready to break free from their shells.
-
Movement: The chicks inside the eggs start making movements as they grow and develop. You may notice the eggs shaking or trembling slightly. These movements are a clear sign that hatching is imminent.
-
Pip marks: Prior to hatching, the chicks create small cracks or holes on the surface of the eggshells using their egg tooth. The appearance of pip marks indicates that the chicks are actively working to emerge from their eggs.
What to Do If the Hatching Process Is Delayed

If the hatching process is delayed, exercise patience and avoid intervening prematurely. Here are steps you can take:
-
Patience is key: Hatching is a natural process that can take time. Give the chicks more time to complete the hatching process.
-
Monitor the nest: Observe any signs of movement or vocalizations from the eggs. Trembling eggs, chirping sounds, or pip marks indicate progress.
-
Avoid interference: Resist the temptation to intervene unless there are clear signs of distress or complications. Allow the chicks to emerge from their eggs on their own.
By understanding the signs of hatching and exercising patience, you can ensure a positive hatching experience for the birds.
Conclusion

Understanding the hatching process of birds provides a fascinating glimpse into the world of avian reproduction. Bird eggs undergo a remarkable transformation from a fragile shell-encased embryo to a fully formed chick ready to face the world.
The hatching process varies among bird species, with incubation periods ranging from 10 to 80 days. Factors such as bird species, environmental conditions, and egg size influence the duration.
During incubation, parent birds provide warmth and maintain optimal conditions for the developing embryos. As the embryo progresses through various developmental stages, it becomes more active and prepares for hatching.
Signs of hatching become apparent as the chick inside the egg uses its egg tooth to crack the shell from the inside. This process, known as pipping, allows the chick to create a small hole through which it can eventually emerge.
Once hatched, the chick may still rely on parental care and protection until it becomes independent. Parent birds provide food, warmth, and guidance to ensure the chick’s survival.
To support successful hatching, provide appropriate nesting sites and minimize disturbance. Maintaining suitable temperature and humidity levels is important. Handling or moving bird eggs should be avoided unless necessary.
By understanding the hatching process and implementing these tips, we can contribute to the successful reproduction and survival of bird populations. Let us appreciate the beauty and complexity of the hatching process and create a nurturing environment for birds to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for bird eggs to hatch in a nest?
The duration of hatching varies among bird species. It can range from as short as 10 to 12 days for small songbirds to as long as 80 days for certain albatross species.
What factors influence the hatching time of bird eggs?
Several factors influence the hatching time of bird eggs. These include temperature, humidity, the number of eggs in the nest, and parental care.
How do birds regulate the temperature in the nest during incubation?
Birds regulate the nest temperature by adjusting their incubation behavior. They take turns sitting on the eggs to provide warmth and maintain the optimal temperature range for embryonic development.
What are the signs that indicate the hatching process is underway?
Signs that indicate the hatching process is underway include vocalizations from the eggs, movements of the chicks inside the eggs, and the appearance of small cracks or holes on the eggshells called pip marks.
Should I intervene if the hatching process is delayed?

It is generally advised to exercise patience and avoid intervening unless there are clear signs of distress or complications. Allowing the chicks to emerge from their eggs on their own is important for their natural development.

Leave a Reply