Introduction

Birds are captivating creatures that mesmerize us with their grace, beauty, and diverse behaviors. In this blog post, we will explore the fascinating world of birds, covering their anatomy, types, colorful feathers, calls and sounds, habitat, migration, and the art of birdwatching. But before we embark on this avian adventure, let’s start with the basics.
What is a bird?
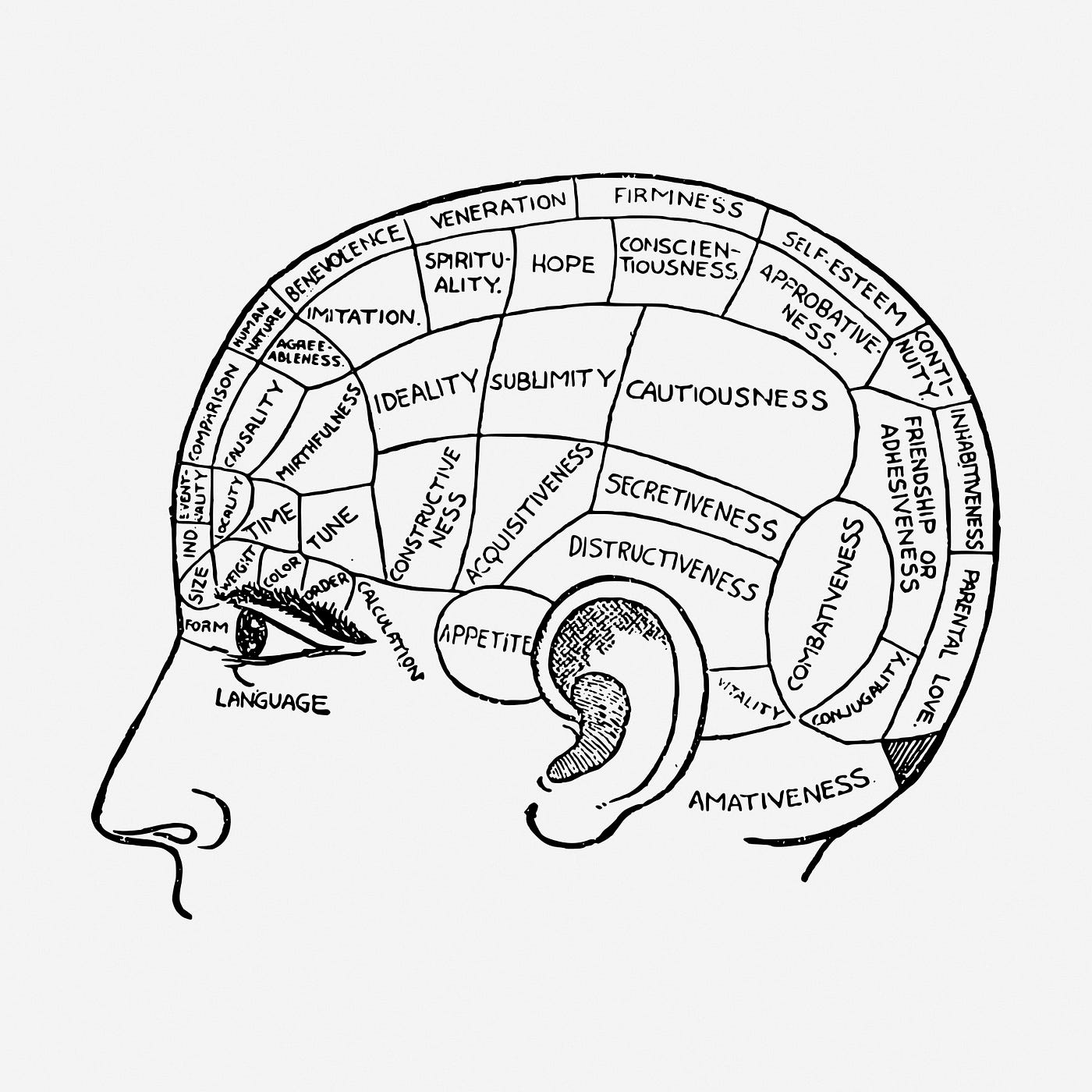
Birds belong to the class Aves, warm-blooded vertebrates with unique characteristics. Renowned for their adaptations for flight, birds have feathers that provide insulation, aid in flight, and display stunning patterns and colors. They also possess specialized beaks for various feeding strategies and lay hard-shelled eggs as part of their reproductive process. Moreover, birds have a distinct skeletal structure with lightweight and hollow bones, enabling agile flight.
The Importance of Describing Birds
Accurately describing birds is invaluable for several reasons. It allows us to vividly depict them in our minds and share that imagery with others. Whether you’re a birdwatcher, an ornithologist, or a nature enthusiast, describing a bird’s appearance, behavior, and unique features enhances our understanding and appreciation of these remarkable creatures.
Furthermore, the ability to identify bird species through description is crucial for birdwatchers and researchers. By noting distinguishing characteristics like coloration, size, and shape, we contribute to scientific research, conservation efforts, and documentation of bird populations and distributions.
Describing birds extends beyond scientific purposes. In literature, poetry, and art, vivid bird descriptions evoke emotions, create imagery, and enhance storytelling. Whether capturing the grace of a soaring eagle or the vibrant plumage of a tropical bird, effective bird descriptions deepen our connection with nature and inspire our creativity.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of birds, starting with their anatomy – from the beak to the feathers, wings, tail, legs, and feet.
The Anatomy of a Bird

Birds possess unique anatomical features that enable them to thrive in their environments. Understanding the various components of a bird’s anatomy provides insights into their behavior, adaptations, and survival strategies.
Beak: Versatile Tools for Survival
The beak, also known as the bill, is a prominent and diverse feature of a bird’s anatomy, shaped by their diet and feeding habits. From stout, powerful beaks that crack open seeds to long, slender beaks that probe for insects, and sharp beaks designed for capturing fish, a bird’s beak is a durable and essential tool for thriving in its ecological niche.
Feathers: More Than Just Flight
Feathers are remarkable structures that contribute to flight, insulation, and communication. They provide insulation through specialized down feathers, enable flight through their arrangement on the wings, and serve as vibrant signals for courtship or camouflage for predator avoidance.
Wings: The Marvel of Flight
Wings are the remarkable feature that allows birds to achieve flight. With primary and secondary feathers providing smooth airflow and lift, wings come in various shapes and sizes, reflecting different flight capabilities and specialized adaptations.
Tail: Agility and Balance in the Air
The tail of a bird plays a vital role in maintaining balance and stability during flight. It also serves as a display of courtship and aids in species identification. The versatility and adaptability of the tail enhance a bird’s overall flying ability and survival strategies.
Legs: Adaptations for Diverse Habitats
Bird legs exhibit remarkable adaptations for thriving in diverse habitats. Whether it’s long, slender legs for wading through marshy environments or strong, muscular legs for capturing prey, bird legs reflect the specific needs and locomotive strategies employed by different species.
Feet: Navigating the Habitat
Bird feet are adapted to suit specific needs, enabling efficient navigation and obtaining food. From grasping feet of birds of prey to webbed feet of waterbirds and specialized perching feet, bird feet align with their ecological niche and lifestyle.
Understanding the intricate anatomy of birds provides valuable insights into their unique adaptations and behaviors. By exploring the beak, feathers, wings, tail, legs, and feet, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable diversity and evolutionary success of avian species.
Types of Birds


Birds are a diverse group of animals, classified into four distinct categories based on their characteristics and behaviors: waterbirds, raptors, perching birds, and game birds.
Waterbirds
Waterbirds have evolved to thrive in aquatic environments such as wetlands, marshes, lakes, rivers, and coastal areas. Notable examples include ducks, geese, swans, herons, egrets, and flamingos. They possess webbed feet for efficient swimming and diving, along with long beaks for catching fish or probing for prey.
Raptors
Raptors, also known as birds of prey, are formidable hunters found in diverse habitats such as forests, grasslands, mountains, and deserts. Majestic birds like eagles, hawks, falcons, owls, and vultures belong to this group. Equipped with sharp beaks, powerful talons, exceptional eyesight, and strong flying abilities, raptors are formidable predators.
Perching Birds
Perching birds, or passerines, represent the largest order of birds. They can be found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas. Sparrows, finches, robins, warblers, and thrushes are examples of perching birds. Their specialized feet with three toes pointing forward and one toe pointing backward enable them to navigate tree canopies and search for food efficiently.
Game Birds
Game birds are primarily hunted for sport or food and can be found in forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas. Pheasants, quails, grouse, and turkeys are common examples. Game birds possess specific adaptations for survival and evasiveness, such as cryptic coloration and swift flight capabilities.
Understanding the different types of birds and their unique characteristics provides a deeper appreciation for the diverse avian world. In the following sections, we will explore other fascinating aspects of birds, including their colorful feathers, vocalizations, habitats, migration patterns, and birdwatching tips.
Colorful Feathers


Birds are known for their stunning and vibrant feathers, which contribute to their visual appeal. Feathers exhibit a wide array of patterns, including stripes, spots, bars, bands, and mottling. These patterns aid in camouflage, courtship displays, and species recognition.
Feathers also display an extensive range of colors, from red, blue, and green to yellow, orange, brown, black, and white. Some birds possess iridescent feathers that shimmer and change color depending on the light angle. Feather colorations play roles in attracting mates, species recognition, and effective camouflage.
The interspecies variation in feather coloration and patterns showcases the incredible diversity and adaptability of birds. It is influenced by factors such as geographic location, habitat, evolutionary adaptations, genetic diversity, environmental factors, and natural selection. This variation highlights the remarkable evolutionary processes that have shaped each species, making them visually captivating and awe-inspiring creatures.
5. Calls and Sounds

Birds are renowned for their captivating vocalizations, producing a diverse range of sounds for various purposes. Understanding these vocalizations provides valuable insights into avian behavior and communication.
Vocalizations

Birds produce a wide range of vocalizations, serving purposes such as communication, territorial defense, and attracting mates. These vocalizations can be categorized into songs and calls.
Songs are melodic and complex, associated with territorial displays and attracting mates. Male birds primarily sing during the breeding season to establish territory and attract females. Songs vary in pitch, rhythm, duration, and tone across species.
Calls are shorter, simpler vocalizations serving functions such as alarm signals, contact calls, and flock communication. Bird calls can vary in pitch, rhythm, duration, and tone across species. They are distinct and sharp, conveying specific messages.
Mating Calls
Mating calls, also known as courtship calls, are specific vocalizations used by birds to attract and communicate with potential mates. These calls have unique patterns, melodies, or repetitions distinct to each species. Male birds use mating calls to establish presence, demonstrate fitness, and attract females. The complexity and intensity of these calls vary widely between species, ranging from soft trills to loud, elaborate songs.
Alarm Calls
Alarm calls are vocalizations used by birds to warn others of potential threats or danger. These calls are typically sharp, abrupt, and repetitive, quickly capturing the attention of other birds. Alarm calls vary in pitch, rhythm, and intensity based on the type of threat. They facilitate communication within bird communities, allowing individuals to alert and coordinate defensive responses.
Understanding bird vocalizations provides insights into behavior, social dynamics, and ecological roles. By deciphering songs and calls, birdwatchers and researchers gain a deeper appreciation for the avian world and contribute to conservation efforts.
The Anatomy of Birds
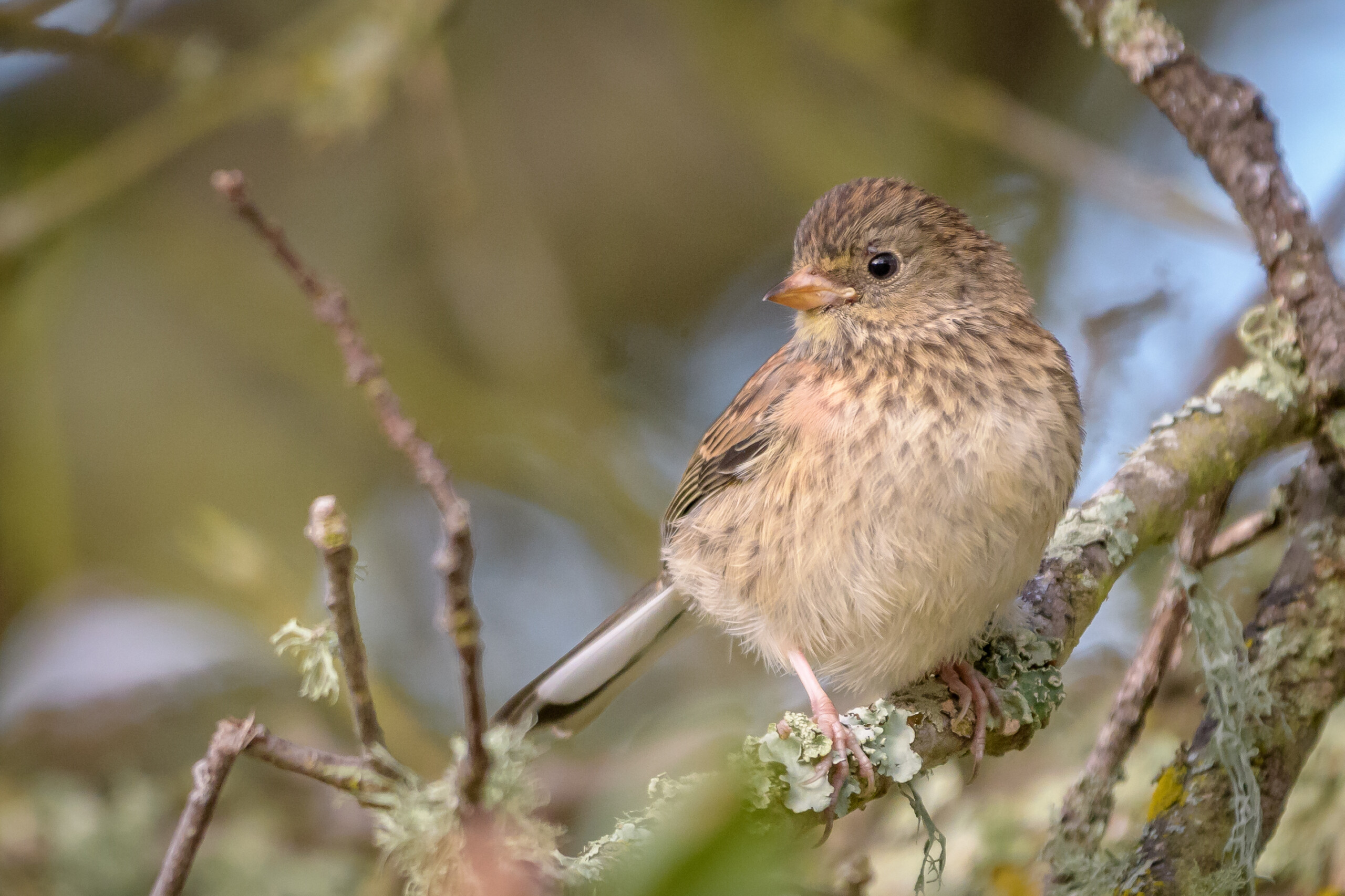

Beak
The beak is a defining feature of a bird’s anatomy, varying in shape and size between species. It serves multiple functions, including feeding, defense, and courtship displays. Beak types range from long and slender for probing flowers or crevices to strong and hooked for tearing flesh. Some birds have specialized beaks for specific diets, such as the finch’s conical beak for cracking seeds or the hummingbird’s long, slender beak for sipping nectar.
Feathers
Feathers are unique to birds and play crucial roles in flight, insulation, and display. They consist of a central shaft with branching barbs. Various types of feathers exist, including contour feathers that provide shape and coloration, down feathers for insulation, and specialized feathers like bristles or filoplumes for sensory purposes. Feathers also exhibit remarkable patterns and colors used for communication and courtship.
Wings
Wings enable birds to fly, with structures adapted to different flight styles. A bird‘s wings consist of long primary feathers attached to the hand bone, secondary feathers along the forearm, and a group of covert feathers covering the base. Birds with long, pointed wings like hawks and falcons are built for swift flight and maneuverability, while those with broad wings like eagles and vultures excel at soaring and gliding.
Tail
The tail of a bird serves various functions, including stability during flight, steering, and communication. Tail shapes can vary greatly, from fan-shaped to forked, graduated, or elongated. Birds like woodpeckers use their stiff tail feathers as support against tree trunks, while birds of paradise have extravagant, elongated tails used in intricate courtship displays. Additionally, tail feathers often contribute to a bird’s overall coloration and patterns.
Legs
Birds’ legs are adapted to their specific lifestyles and habitats, exhibiting characteristics such as length, strength, and foot structure. Wading birds like herons have long, slender legs for walking through shallow waters, while birds of prey have powerful legs and sharp talons for capturing prey. Some birds have specialized adaptations like webbed feet for swimming or feet with sharp claws for perching or climbing.
Feet
Birds’ feet exhibit remarkable diversity in structure and function, adapted for various purposes such as swimming, perching, grasping prey, or climbing trees. For example, waterbirds like ducks have webbed feet for efficient swimming, while perching birds have feet designed for gripping branches. Raptors have strong, sharp talons for capturing and holding prey, and birds like woodpeckers have strong, claw-like feet for clinging to tree trunks.
Types of Birds
Waterbirds
Waterbirds are a diverse group of birds that inhabit aquatic environments, including ducks, geese, swans, herons, egrets, and others. They have adaptations for swimming, such as webbed feet or long legs for wading. Waterbirds can be found in freshwater habitats like lakes and rivers, as well as coastal areas and wetlands.
Raptors
Raptors, also known as birds of prey, are characterized by their sharp beaks and strong, curved talons. They include eagles, hawks, falcons, and owls. Raptors are skilled hunters with excellent vision for detecting prey from a distance. They can be found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and mountainous regions.
Perching Birds
Perching birds, also known as passerines, make up the largest order of birds and include sparrows, finches, warblers, and robins. They are characterized by their specialized feet with three forward-facing toes and one backward-facing toe, allowing them to perch on branches. Perching birds have diverse diets and can be found in various habitats, including forests, woodlands, gardens, and urban areas.
Game Birds
Game birds are a group of birds hunted for sport or food, including pheasants, quails, turkeys, and grouse. They often have sturdy bodies, strong legs, and short, rounded wings, enabling them to take off quickly and navigate through dense vegetation. Game birds are adapted to terrestrial habitats such as grasslands, forests, and agricultural fields.
Colorful Feathers
Patterns
Birds display a remarkable array of patterns on their feathers, serving purposes like camouflage, communication, and courtship displays. Camouflage patterns help birds blend into their surroundings, making them less visible to predators or prey. Other patterns, such as eye spots or bold stripes, startle or deter predators.
Colorations
Birds exhibit a wide range of colors on their feathers, from vibrant hues to subtle shades. Coloration serves functions like attracting mates, establishing territory, or signaling social status. Many male birds have bright and striking plumage used in courtship displays. Female birds often have more subdued colors to provide camouflage while nesting.
Interspecies Variation
Birds within the same species can exhibit significant variations in coloration and patterns influenced by factors like age, sex, geographic location, and genetic diversity. Some birds undergo plumage changes during different life stages, transitioning from juvenile to adult plumage. Interspecies variation allows birds to adapt to different environments and plays a role in sexual selection and species recognition.
(Word count: 479 words)
Migration

Migration is a fascinating behavior observed in many bird species. It involves the seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds, providing valuable insights into their remarkable journeys.
Patterns
Migration patterns vary among bird species. They can occur over short distances or cover thousands of miles. Some birds migrate in large flocks, while others migrate individually or in smaller groups. These patterns are influenced by factors such as food availability, weather conditions, and geographic barriers.
Birds follow specific migration routes known as flyways, which act as highways in the sky. The choice of flyway depends on habitat requirements and geographical obstacles.
Adaptations
Birds have evolved remarkable adaptations to facilitate migration. Physical adaptations, such as streamlined bodies and long, pointed wings, reduce drag and enable sustained flight. Physiological adaptations involve increasing fat storage as energy reserves. Behavioral adaptations include navigation using celestial cues, landmarks, and Earth’s magnetic field, as well as adjusting flight speed and altitude to conserve energy.
Arctic terns are an example of a species that undertakes extraordinary migrations, covering a staggering round-trip distance of over 40,000 miles. These adaptations enable birds to successfully complete their migratory journeys and thrive in different habitats.
Understanding migration patterns and adaptations highlights the resilience and adaptability of avian species in their quest for survival.
Birdwatching
Birdwatching is a popular activity that allows enthusiasts to observe and appreciate the diverse avian species in their natural habitats. By developing identification skills, acquiring necessary equipment, and following essential tips, you can enhance your birdwatching experience.
Identifying Birds
Identifying birds requires keen observation and attention to detail. Observe size, shape, coloration, markings, behavior, and listen to calls or songs. Use a field guide or bird identification app and consider the bird’s habitat.
Equipment Needed
Essential equipment for birdwatching includes binoculars, a field guide or bird identification app, a notebook and pen for recording observations, and optionally, a camera with a telephoto lens.
Tips for Birdwatching

Choose the right time, be patient and observant, and learn bird behavior. Familiarize yourself with foraging techniques, flight patterns, and feeding preferences.
By honing your bird identification skills, equipping yourself with necessary tools, and applying effective birdwatching strategies, you’ll enhance your appreciation for these fascinating creatures and gain a deeper understanding of their natural world.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding how to identify birds and engaging in birdwatching can be a rewarding experience. By observing their unique features, colors, and behaviors, you can develop a deeper appreciation for the avian species around you. Remember to carry the essential equipment, utilize field guides or identification apps, and practice patience and observation while birdwatching. So, grab your binoculars, field guide, and notebook, and embark on an exciting journey into the world of birds. Happy birdwatching!
Conclusion
In this exploration of how to describe a bird, we have delved into the fascinating world of avian anatomy, behavior, and habitats. By understanding the intricacies of these remarkable creatures, we develop a deeper appreciation for their beauty and importance in our natural environment.
Throughout our journey, we discovered the diverse array of features that make each bird species unique. From beaks and feathers to wings, tails, legs, and feet, birds possess adaptations that enable them to thrive in various environments. Their colorful plumage showcases the captivating beauty of interspecies variation.
Moreover, we explored the vocal world of birds, from melodic songs to distinctive calls. These vocalizations serve multiple purposes, including communication, mating rituals, and warning signals. Listening to the symphony of bird sounds offers insights into their behavior and ecological roles.
Understanding a bird’s habitat is crucial to appreciating its lifestyle and survival strategies. Birds have adapted to diverse ecosystems worldwide, from lush forests to tranquil wetlands and expansive skies. They contribute to the intricate web of life on our planet.
We also touched upon the phenomenon of migration, where birds embark on incredible journeys across vast distances. Their navigation abilities and physical adaptations enable them to overcome challenges and find suitable breeding and feeding grounds. Migration stands as a testament to their resilience and adaptability in the face of changing seasons and environmental conditions.
To fully immerse ourselves in the world of birds, we explored the art of birdwatching. By learning to identify birds and equipping ourselves with the necessary tools, we can embark on thrilling adventures in the great outdoors. Patient observation and appreciation of their behaviors and habitats allow us to cultivate a deep connection with nature and contribute to bird conservation efforts.
In conclusion, birds are a testament to the wonders of the natural world. By sharpening our descriptive skills, we can capture the essence of these remarkable creatures, their physical attributes, and behaviors. Let us continue to explore and appreciate the avian world, fostering a sense of wonder and curiosity that inspires us to protect and preserve these magnificent beings. May the enchanting realm of birds forever captivate our hearts and minds.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features to describe when identifying a bird?
When identifying a bird, key features to describe include its size, shape, coloration, markings, behavior, habitat, and vocalizations. Pay attention to the bird’s beak shape, feathers, wings, tail, legs, and feet. Additionally, note any unique patterns or colors on the bird’s plumage.
How can I effectively describe a bird’s appearance?
To effectively describe a bird’s appearance, use descriptive language to convey its size, shape, and coloration. Describe the bird’s beak shape, feather patterns, and any distinct markings or colors on its plumage. Pay attention to details such as eye color, leg length, and any special features like crests or facial markings.
What are some tips for describing a bird’s behavior?
When describing a bird’s behavior, observe its movements, foraging techniques, flight patterns, and vocalizations. Note whether the bird is solitary or in a group, its feeding habits, and any unique behaviors such as courtship displays or territorial defense. Describing the bird’s behavior helps paint a vivid picture of its interactions with its environment.
How can I describe a bird’s habitat?
To describe a bird’s habitat, focus on the type of ecosystem or environment where the bird is commonly found. Describe the vegetation, geographical features, and other elements of the habitat that are relevant to the bird’s survival and behavior. Consider the bird’s preference for forests, wetlands, grasslands, or coastal areas, and mention any specific adaptations it has for its habitat.
What are some descriptive words and phrases to describe birds?
When describing birds, you can use descriptive words and phrases such as graceful, majestic, vibrant, iridescent, melodious, agile, intricate, striking, camouflaged, and diverse. Consider using adjectives that capture the bird’s appearance, behavior, or unique features. Use similes or metaphors to paint a vivid picture of

Leave a Reply